Why Machinists Need These BI Tools: Enhancing Efficiency and Accuracy
In the demanding world of precision manufacturing, machinists are constantly striving for excellence. They aim to create intricate parts with utmost accuracy and efficiency. However, navigating complex data and optimizing workflows can be challenging. This is where Business Intelligence (BI) tools come into play. These tools offer machinists powerful capabilities to analyze data, improve decision-making, and ultimately, boost their performance. This article explores why machinists need these BI tools and how they can revolutionize their operations.
Understanding the Machinist’s Challenges
Machinists face a unique set of hurdles. They grapple with intricate designs, tight tolerances, and the pressure to deliver high-quality products on time. They often work with large volumes of data from various sources. This includes Computer-Aided Design (CAD) files, Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) programs, and machine performance metrics. Sifting through this data can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Without proper tools, machinists may struggle to identify bottlenecks, predict potential issues, and optimize their processes. The need for data-driven insights is crucial for success. These insights drive efficiency and profitability.
The Power of Business Intelligence in Machining
BI tools transform raw data into actionable insights. They provide machinists with a clear understanding of their operations. These tools offer a range of functionalities that directly benefit the machining process:
- Data Aggregation and Integration: BI tools can gather data from diverse sources. This includes machine sensors, ERP systems, and quality control databases. This unified view eliminates the need to manually collect and consolidate data.
- Data Visualization: Complex data becomes easy to understand through interactive dashboards and charts. Machinists can quickly identify trends, anomalies, and areas for improvement.
- Performance Monitoring: Real-time tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential. Machinists can monitor machine uptime, production rates, and material usage. This enables proactive problem-solving.
- Predictive Analytics: BI tools leverage advanced analytics to forecast future outcomes. Machinists can anticipate equipment failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and improve inventory management.
- Reporting and Analysis: Generating comprehensive reports on production, costs, and quality is simplified. This supports data-driven decision-making and strategic planning.
Key BI Tools for Machinists
Several BI tools are specifically designed or well-suited for the machining industry. These tools offer features tailored to the unique needs of machinists. Some popular options include:
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization and analytics platform. It allows machinists to create interactive dashboards and explore data in detail.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s BI tool offers a user-friendly interface and robust data analysis capabilities. It integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products.
- Qlik Sense: This tool provides associative data discovery and advanced analytics features. It helps machinists uncover hidden insights and patterns.
- Specialized Manufacturing BI Solutions: Several vendors offer BI solutions specifically designed for the manufacturing sector. These tools often include pre-built dashboards and reports.
How Machinists Can Benefit from BI Tools
The advantages of using BI tools are numerous. They touch upon nearly every aspect of a machinist’s work. Here are some of the key benefits:
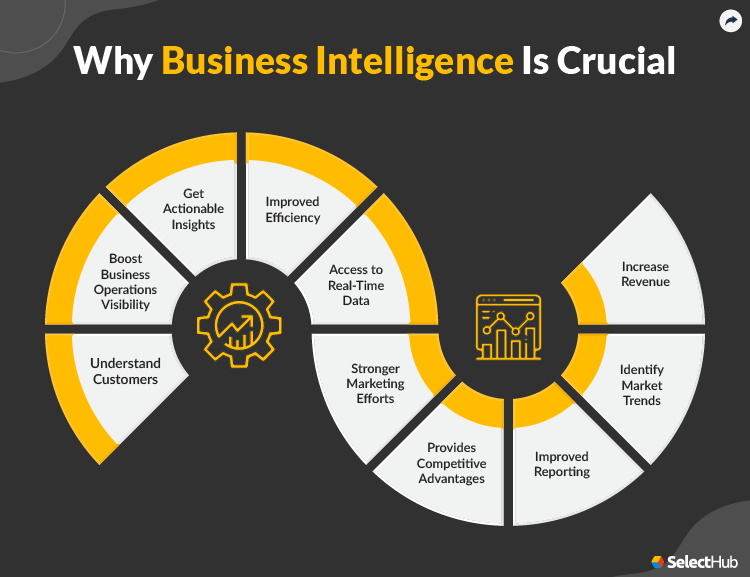
- Improved Efficiency: By identifying bottlenecks and optimizing workflows, BI tools help machinists streamline their operations. This leads to faster production cycles and reduced lead times.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Data-driven insights enable machinists to make more informed decisions. This improves precision and reduces the risk of errors.
- Reduced Costs: By optimizing material usage, minimizing waste, and predicting equipment failures, BI tools help machinists reduce operational costs.
- Increased Productivity: Real-time monitoring of machine performance and proactive problem-solving contribute to higher productivity levels.
- Better Decision-Making: With access to comprehensive data and insightful analytics, machinists can make more informed decisions. This leads to better outcomes and improved profitability.
- Improved Quality Control: BI tools allow machinists to monitor quality metrics in real-time. This enables faster identification and resolution of quality issues.
Implementing BI Tools: A Practical Guide
Implementing BI tools involves several steps. These steps ensure a successful integration and maximum benefit for machinists:
- Define Objectives: Clearly identify the goals you want to achieve with BI tools. This could include improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing quality.
- Assess Data Sources: Determine the data sources you need to integrate into your BI system. These might include machine sensors, ERP systems, and quality control databases.
- Choose the Right Tool: Select a BI tool that meets your specific needs and budget. Consider factors such as ease of use, features, and integration capabilities.
- Implement the Tool: Set up the BI tool and connect it to your data sources. Configure dashboards and reports to monitor key performance indicators.
- Train Users: Provide adequate training to machinists and other users on how to use the BI tool effectively.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the performance of your BI system and make adjustments as needed. This ensures that you are maximizing its value.
Case Studies: BI in Action
Several machining companies have successfully implemented BI tools. They have achieved significant improvements in their operations. Here are a couple of examples:
- Company A: This company used BI tools to monitor machine uptime and identify areas of downtime. By addressing the root causes of these issues, they increased machine utilization by 15%.
- Company B: This company implemented BI tools to analyze material usage. They identified opportunities to optimize their inventory management. This resulted in a 10% reduction in material costs.
These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits that BI tools can bring to the machining industry. Machinists can leverage data-driven insights to improve their efficiency, accuracy, and profitability.
The Future of Machining and BI
The integration of BI tools in the machining industry is only going to grow. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more sophisticated BI solutions. These solutions will offer enhanced capabilities. This includes:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms will further automate data analysis. They will provide even more accurate predictions and insights.
- Real-time Data Streaming: The ability to stream data in real-time will provide machinists with instant insights. They can make immediate adjustments to their operations.
- Cloud-Based BI: Cloud-based BI solutions will become more prevalent. This will offer greater accessibility and scalability.
- Integration with IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) will play a larger role. This is in collecting data from a wider range of sources.
Machinists who embrace these advancements will gain a competitive edge. They will be better equipped to meet the challenges of the future.
Conclusion: Embracing BI for Machining Success
In conclusion, BI tools are essential for modern machinists. They provide the insights and capabilities needed to thrive in a competitive industry. By embracing these tools, machinists can improve efficiency, accuracy, and profitability. They can also make better decisions. The future of machining is data-driven. Machinists who harness the power of BI will be well-positioned for success. This means machinists should adopt BI tools to improve their performance. The benefits of BI tools are clear. Why machinists need these BI tools is evident.
[See also: Related Article Titles]