Business Intelligence Tools to Track Preservation: Safeguarding Assets in the Modern Era
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and increasing complexity, the preservation of assets, be they financial, physical, or intellectual, has become paramount. The effective tracking of these assets, ensuring their longevity and value, is no longer a matter of simple oversight. It demands sophisticated strategies and tools. This is where Business Intelligence (BI) tools come into play, offering a powerful means to monitor, analyze, and ultimately, preserve crucial resources.
This article delves into the realm of Business Intelligence tools to track preservation. We will explore how these tools are transforming asset management across various industries, providing insights into their functionality, benefits, and the crucial role they play in safeguarding resources against potential threats.
The Imperative of Asset Preservation
The concept of asset preservation extends far beyond mere protection. It encompasses the proactive management of resources to mitigate risk, optimize performance, and ensure long-term sustainability. Failing to effectively preserve assets can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and even operational failures.
The challenges of asset preservation are multifaceted. They include:
- Complexity of Modern Assets: Assets are increasingly intricate and interconnected, making them harder to monitor.
- Evolving Threats: Risks such as cyber threats, natural disasters, and market volatility constantly emerge.
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict regulations demand meticulous tracking and documentation.
- Data Overload: Organizations grapple with massive amounts of data, making it difficult to extract actionable insights.
To overcome these challenges, organizations require robust solutions that provide a comprehensive view of their assets and the ability to proactively manage them. Business Intelligence tools to track preservation offer precisely that.
Understanding Business Intelligence Tools
Business Intelligence tools are software applications designed to collect, process, analyze, and visualize data. They transform raw data into actionable insights that can inform decision-making. These tools are used across a wide range of industries and functions.
Key functionalities of BI tools include:
- Data Integration: The ability to gather data from various sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and cloud platforms.
- Data Warehousing: The storage and organization of large datasets for analysis.
- Data Analysis: The use of statistical methods and algorithms to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies.
- Reporting and Visualization: The creation of dashboards, reports, and charts to communicate insights effectively.
These features enable organizations to gain a deeper understanding of their assets, identify potential risks, and make informed decisions to protect them. The application of Business Intelligence tools to track preservation directly enhances asset management strategies.
Key Business Intelligence Tools for Asset Preservation
Several BI tools are particularly well-suited for asset preservation. These tools offer a range of features that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different organizations. The selection of the right tool will depend on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the specific assets being tracked.
Data Visualization Software
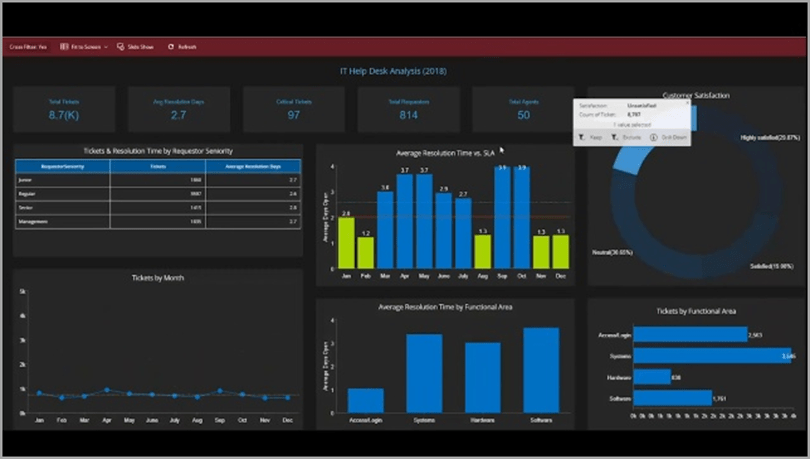
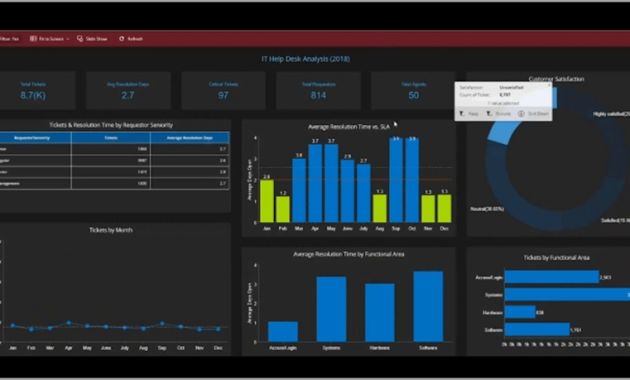
Tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense excel at transforming complex data into easy-to-understand visuals. This allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the status of assets and identify potential issues. These tools provide dashboards that can be customized to track relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and generate alerts when thresholds are crossed.
Data Mining and Predictive Analytics Platforms
Platforms like RapidMiner and KNIME allow for advanced data analysis. They enable organizations to identify hidden patterns and predict future events. This is crucial for anticipating asset failures, optimizing maintenance schedules, and mitigating risks. These platforms use advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze data. This helps to uncover insights that would be impossible to find through manual analysis.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems, such as SAP and Oracle, integrate various business functions. They provide a centralized view of assets, including their location, condition, and maintenance history. ERP systems can generate reports, track depreciation, and provide insights into asset utilization. This information is vital for making informed decisions about asset management. These systems are essential components of Business Intelligence tools to track preservation.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS tools are used to map and analyze geographical data. They are particularly useful for tracking physical assets, such as pipelines, infrastructure, and real estate. By integrating asset data with location information, organizations can gain a better understanding of their assets’ physical environment. This facilitates risk assessment and resource allocation. GIS tools are increasingly integrated with other BI platforms for comprehensive asset management.
Benefits of Using Business Intelligence Tools for Preservation
The adoption of Business Intelligence tools to track preservation offers a multitude of benefits, leading to more efficient and effective asset management strategies. These tools provide a significant return on investment by improving asset performance and reducing risks.
- Improved Decision-Making: BI tools provide data-driven insights that enable informed decisions about asset allocation, maintenance, and disposal.
- Reduced Costs: By optimizing maintenance schedules and preventing asset failures, BI tools help to reduce operational costs.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks related to asset performance.
- Increased Efficiency: Automating data collection and analysis, freeing up resources for other tasks.
- Better Regulatory Compliance: Streamlining reporting and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Improved Asset Utilization: Optimizing the use of existing assets to maximize their value.
These benefits contribute to a more resilient and sustainable organization, capable of weathering economic fluctuations and other challenges.
Implementing Business Intelligence Tools for Preservation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing BI tools for asset preservation requires a strategic approach. The following steps provide a framework for successful implementation:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the goals of the implementation, such as reducing maintenance costs or improving asset uptime.
- Assess Current State: Evaluate the existing asset management processes and data sources.
- Select the Right Tools: Choose BI tools that align with the organization’s needs and budget.
- Data Integration: Integrate data from various sources into the BI platform.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Develop dashboards and reports to track key performance indicators.
- Training and Adoption: Train employees on how to use the new tools and processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation and make adjustments as needed.
By following these steps, organizations can ensure that their BI implementation is successful and delivers the desired results. The effective implementation of Business Intelligence tools to track preservation is crucial for long-term success.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Business Intelligence
Several organizations have successfully used BI tools to improve their asset preservation strategies. These case studies highlight the tangible benefits of implementing these tools.
Case Study 1: Manufacturing A manufacturing company used Power BI to track the performance of its equipment. They identified patterns of equipment failure. This allowed them to implement a predictive maintenance program, reducing downtime by 20% and saving thousands of dollars in repair costs.
Case Study 2: Utilities A utility company used GIS to monitor its infrastructure. They identified high-risk areas for pipeline failures. This enabled them to prioritize inspections and repairs, reducing the risk of environmental damage and improving public safety.
Case Study 3: Financial Services A financial institution utilized a BI platform to monitor its real estate portfolio. They analyzed market trends and property values. This helped them make informed decisions about acquisitions, sales, and property management.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of Business Intelligence tools to track preservation across different industries.
The Future of Business Intelligence in Asset Preservation
The future of Business Intelligence tools to track preservation is bright. Several trends are poised to further enhance their capabilities:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML will play an increasingly important role in automating data analysis. They will also help predict asset failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
- Cloud-Based BI: The adoption of cloud-based BI platforms will continue to grow, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
- Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT): The integration of BI tools with IoT devices will enable real-time monitoring of assets. This will provide valuable data for predictive maintenance.
- Increased Focus on Data Governance: With the growing volume of data, data governance will become increasingly important.
These trends will empower organizations to further enhance their asset preservation strategies and achieve even greater levels of efficiency and effectiveness.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Business Intelligence
In conclusion, Business Intelligence tools to track preservation are essential for organizations seeking to safeguard their assets in the modern era. By providing actionable insights and enabling proactive management, these tools empower organizations to mitigate risk, optimize performance, and ensure long-term sustainability. As technology continues to evolve, the role of BI in asset preservation will only become more critical.
Organizations that embrace these tools will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly complex and competitive environment. The future of asset management is undoubtedly linked to the power of data and the insights it provides. [See also: Related Article Titles]